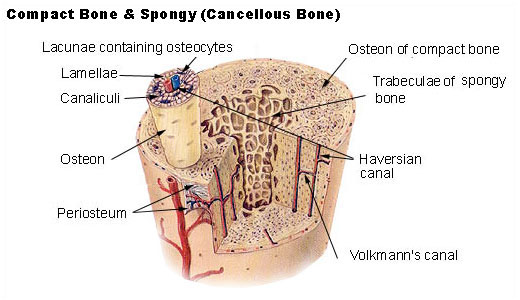
Osteons are absent in spongy bones instead they contain lamellae arranged in the lattice of trabeculae from where they receive nutrients via blood supply. Spongy and compact bones are two basic structural bone types.
Seer Training Structure Of Bone Tissue
Difference Between Spongy and Compact Bones Bones are the primary skeletal structure that supports muscles and gives shape to the body.

. It contains inner layers of. Spongy bone consists of plates trabeculae and bars of bone adjacent to small irregular cavities that contain red bone marrow. Spongy bone is commonly observed on the ends of lengthy bones the epiphyses surrounded by using tougher compact bone.
Bone is hard and many of its functions depend on that characteristic hardness. Spongy bone contains trabeculae perforated tissue with connecting rods and plates. Instead the lacunae and osteocytes are found in a lattice-like network of matrix spikes called trabeculae singular trabecula Figure 638.
The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of. The branched bony trabeculae anastomose with other branches of trabeculae. The spongy bone consists of plates or the trabeculae and the bars of the bones which are adjacent to the small irregular cavities that contain the red bone marrow.
Each trabecula of the spongy bone is made of several parallel lamellae of the bony matrix. Storage of Bone Marrow. 21 rows The wider section at each end of the bone is called the epiphysis plural epiphyses which is.
It is highly vascularized and has red bone marrow. Hematopoiesis takes place here or fat cells might be stored depending on the location. They make up the long bones in the body.
Bone marrow also called myeloid tissue is formed when the trabecular matrix crowds blood vessels together and they condense. Long bones are dense hard bones that provide strength structure and mobility. Spongy bone is the inner framework of the bone in which the bone marrow resides.
The spongy bone is a much porous kind of bone which is found in the animals. The ground substance of bone is arranged in concentrated layers lamellae round the small canals which run parallel to the long axis shaft of the bone. Spongy bone has a lattice like look due to the presence of a complicated network of.
The interior portion of the long bones is composed of spongy bones. They are also called cancellous bones. The spongy bone is made up of cells known as Osteocytes which lie in small cavities called.
Outside all of bone is a connective tissue sheath called the periosteum see below photograph. Spongy bone is found inside bones and is lighter and less dense than compact bone. Microscopically compact bone has the features elucidated in the video osteons while the spongy bone is less dense and shows a framework of trabeculae.
It is present beneath the compact bone and contains red bone marrow or yellow bone marrow in its spaces. The trabeculae are arranged in an orderly manner to provide maximum strength. Reduces the Weight of the Skeleton.
Spongy bone is light and porous and found in most parts of the body and in other bones that do not typically endure large volumes of mechanical stress. Spongy bone is weaker and softer than compact bone however its far greater flexible. Spongy cancellous bone is lighter and less dense than compact bone.
Osteocytes can be seen in layers in adult spongy bone. Structure of Spongy Bone. The Interior part of the bone is formed by spongy bone.
It is usually situated at the ends of long bones with the harder compact bone which surrounds it. Functions of Spongy. These trabeculae enclose the irregular marrow cavities between them which contain blood vessels.
This spongy bone is made of slender bony trabeculae that may be single or branched. 2 votes See 1 more reply. Describe how bones are nourished and innervated.
These canals called Haversian canals are. The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. The matrix of the bone is composed of mineral bars called trabeculae which forms a three-dimensional latticework.
Spongy bone also called cancellous or trabecular bone provides structural support and facilitates movement of the joints and limbs. Structure of Cancellous Bone Cancellous bone is also known as spongy bone because it resembles a sponge or honeycomb with many open spaces connected by flat planes of bone known as trabeculae. Periosteum is a tough fibrous membrane that covers and protects the outer surfaces of bone.
Functions of Spongy Bone. Bone tissue osseous tissue differs greatly from other tissues in the body. A long bone has two parts.
The Spongy bone tissue looks spongy but its texture is not spongy as it contains more spaces in its structure. Spongy Bone Spongy Bone Definition. Spongy Cancellous Bone Like compact bone spongy bone also known as cancellous bone contains osteocytes housed in lacunae but they are not arranged in concentric circles.
Identify the structures that compose compact and spongy bone. Between trabeculae are the spaces filled with marrow. Spongy bone is a very porous type of bone which is generally found in animals.
Bone marrow is a soft connective tissue that produces blood cells. It could also be determined in the vertebrae the ribs the skull and the joint bones. Trabeculae consist of lamellae and osteocytes.
The canaliculi connect to the adjacent cavities instead of a central haversian canal to receive their blood supply. It can be found inside the vertebrae ribs skull and joints of the body. Red bone marrow is found between the trabuculae.
The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone Figure 1. Spongy bone tissue does not contain osteons that constitute compact bone tissue. Trabeculae of spongy bones do not have blood vessels and a central canal.
Spongy bones are less dense and lighter than compact bones. A typical long bone shows the gross anatomical characteristics of bone. Instead it consists of trabeculae which are lamellae that are arranged as rods or plates.
This is because spongy bone is porous. Spongy bone contains large marrow spaces defined by shelves and spicules of bone. Spongy bone is the osseous tissue found in the middle of the bones.
It is found inside the pores of spongy bone. Adds Strength and Flexibility to Bones. The inner space is lined by osteoblasts and osteoclasts called the endosteum.
Located in head of femur--head of tibia-- skull--found in areas of low stress force can resist force in many directions spongy bone weight much lighter than compact bone--reduces the weight of the skeleton--due to number os spaces spongy bone contains consists of red bone marrow--formation of red blood cells--white blood cellsplatlets. Blood vessels within this tissue deliver nutrients to osteocytes and remove waste. The diaphysis and the epiphysis.

Spongy Bone Cancellous Bone Definition Function Biology

Cancellous Bone Anatomy Britannica

Bone Spongy And Compact Structure Of Spongy Bone Bones Anatomy Bones Human Skeleton Anatomy
0 Comments